Networks and Routing
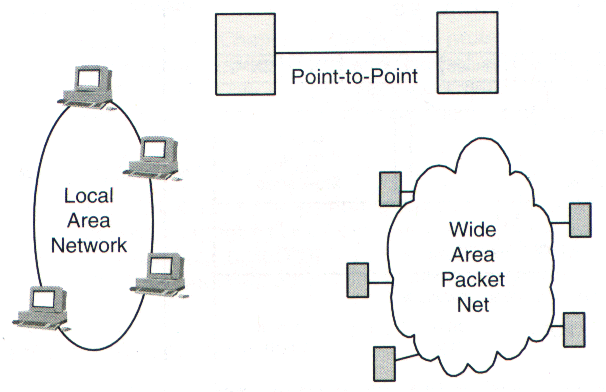

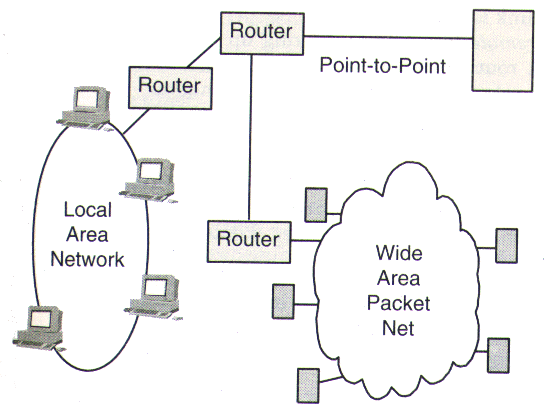
Networks are joined into an internet by IP routers.
IP software runs in hosts and IP routers.
If the destination for a datagram is not on the same link as the source host, IP in the host directs the datagram to a local router.
IP looks up network addresses in a routing table to connect to remote destinations.
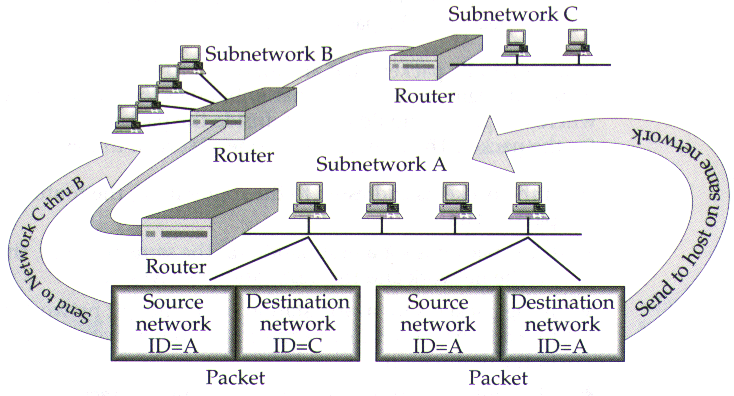
each node on the Internet (or any internet) has a unique IP address, which is a 4-byte address, consisting of two parts: network ID, host ID
written as 4 numbers, separated by dots:
e.g. 192.197.62.35,
read as "192 dot 197 dot 62 dot 35"
there are three common address classes:
each host has in an organization belongs to a domain and
has a unique hostname
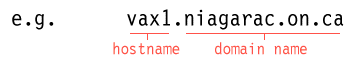
names get translated into IP addresses using the Domain Naming System (DNS)

 Back to the ELNC1221 Page
Back to the ELNC1221 Page